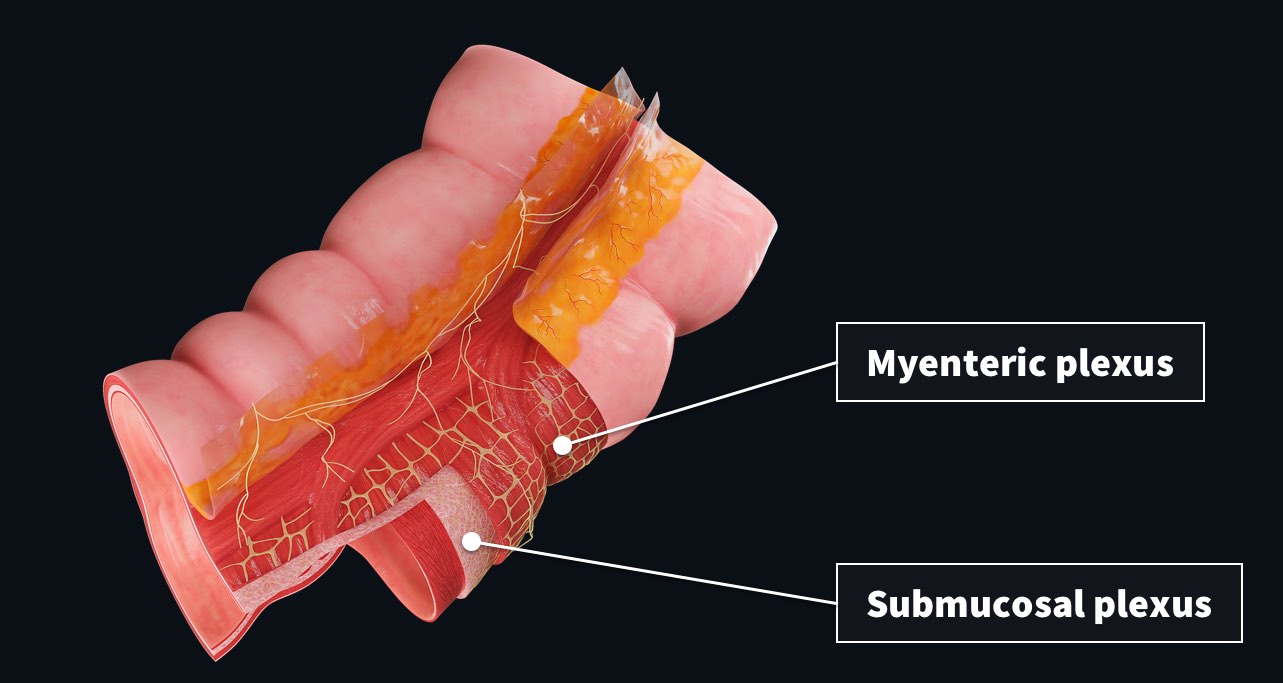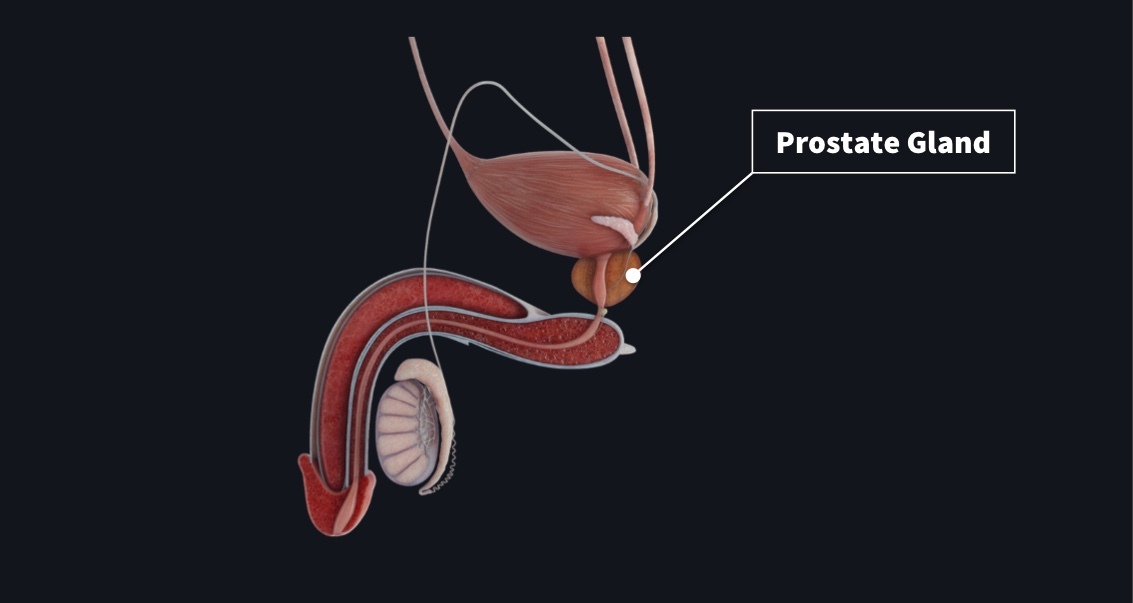
Prostate cancer is the second most common cancer in men globally ??, and according to the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention (CDC), out of every 100 American men, about 13 will get prostate cancer during their lifetime. Of that about 2-3 men may die from prostate cancer. READ POST